Just how wrong were those SPAC projections?
Why are companies that went public via SPACs struggling? Did they catch a headwind from changing market conditions that previously pushed them forward? You bet. But the damage is also self-inflicted.
The SPAC boom is behind us. The effort to leverage blank-check companies to take private companies public failed to clear the unicorn backlog, and a great number of combinations have lost value.
Examples abound. Latch is now worth around $4 per share, for example. MetroMile is worth $1.27 per share. The list goes on.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on TechCrunch+ or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
Why are companies that went public via SPACs struggling so much? Did they catch a headwind from changing market conditions that previously helped push them forward? You bet.
 But the damage is also self-inflicted. Since 2022 kicked off, I’ve been waiting for earnings season to wrap so that we could execute a meta-analysis of SPAC earnings, essentially contrasting 2021 results with prior projections. Recall that many SPAC investor presentations painted a picture of essentially vertical growth.
But the damage is also self-inflicted. Since 2022 kicked off, I’ve been waiting for earnings season to wrap so that we could execute a meta-analysis of SPAC earnings, essentially contrasting 2021 results with prior projections. Recall that many SPAC investor presentations painted a picture of essentially vertical growth.
The pitch was pretty simple: This neat, young company is going to combine with a SPAC, raise a bunch of cash, and then grow like all hell. So what actually happened? Not that.
The Wall Street Journal did the work I had in mind before me, so let’s listen in:
Nearly half of all startups with less than $10 million of annual revenue that went public last year through a special-purpose acquisition company, known as SPAC, have failed or are expected to fail to meet the 2021 revenue or earnings targets they provided to investors, according to a Wall Street Journal analysis.
Even more, the Journal found that the companies that have or likely will wind up short of their 2021 targets are going to do so by some 53%. These are not small misses, in other words, but wide, embarrassing fuckups.
AppHarvest, a company that the Journal calls out, is a good example of the issue. Back in 2020, AppHarvest pitched its SPAC combination with the following chart:
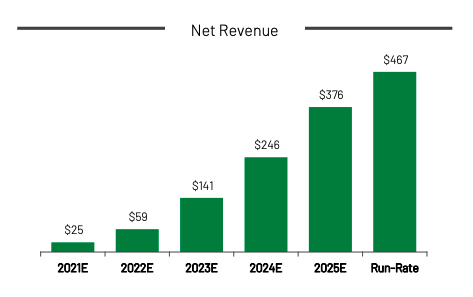
Image Credits: AppHarvest investor presentation
I mean, who wouldn’t want to invest in that company? It’s going to double in 2022 from a comfortable revenue base, more than double in 2023, and then accrete more than $100 million in revenue for the following two years. AppHarvest promised a rocketship that you could buy into.
So what actually happened? The Exchange pulled the company’s earnings results and here’s the data:







